Reviews and corrects ledger-to-subledger alignment in D365 by fixing posting configurations, inventory profiles, reconciliation logic, GL mapping, and critical reporting procedures.
What is EDI?
Posted on: July 17, 2024 | By: Meaghan Andrews | QAD Business Process
EDI – Electronic Data Interchange – A form of electronic communication created in the 1960’s to improve the supply chain efficiency and communication. EDI has since evolved to a more wide-spread business to business communication tool integrating more and more trading partners in new ways. Today’s EDI leverages more API integration points to various business, storefronts, shipping carriers, and more across a vast number of industries.
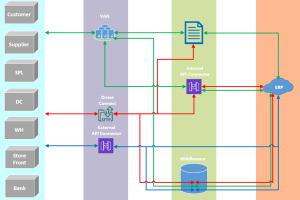
EDI is transmitted in several standards today, which include ANSI X12, EDIFACT, VDA, Odette, TRADACOMS and ebXML to name a few. Within each standard there have been many different versions created over the years. Various trading partners (business partners exchanging these business documents) will either agree on which standard and version to exchange or it is often dictated by the customer side of the engagement.
Once the standard is identified, then the partners will set up a means of communication to transmit the documents between one another. Typically, a VAN (Value Added Network) is leveraged at a cost to provide a mailbox for each partner to send/receive the documents. Some other ways may be a direct connection via SFTP SSH, OFTP, AS2, external APIs, or other agreed upon secure internet protocols the partners can perform.
EDI Documents are composed of an envelope that aids in transmitting and routing the document to the correct trading partner ID’s. The body of the document will entail more intricate information to the actual purpose of the document. A business will typically leverage parts of the standard format that suits their business needs allowing for the receiving partner to best interpret and pull the data required out of it. How a business uses the standard format is often detailed in a partners EDI implementation guide that they provide for clearer definition of what is to be transmitted within it.
EDI Benefits
A well-orchestrated EDI solution can have many benefits:
- Efficiency as it allows for a higher volume of data to be processed within the system in a quicker timeframe
- Accuracy in data as it is loaded directly from the transactional document versus hand entered
- Cost savings as it removes the need for additional resources to perform manual data entry and paperwork to manage the same transactions
- Speed in the access of data as automation of the transactions can greatly increase the time in which it is loaded/unloaded from the system
Conclusion
In conclusion, an efficient well-constructed EDI solution is one that is well thought out and designed to suit the needs of the business and their business partners and can bring many benefits. A business should however evaluate the overall need to ensure that a good business case supports the cost benefit of implementing the solution.
Next Steps
If you are interested in learning more about EDI, contact us here to find out how we can help you grow your business. You can also email us at info@loganconsulting.com or call (312) 345-8817.